World Heritage Identification Number: 1430
World Heritage since: 2013
Category: Natural Heritage
Transboundary Heritage: No
Endangered Heritage: No
Country: 🇳🇦 Namibia
Continent: Africa
UNESCO World Region: Africa
Map
The Namib Sand Sea: A Unique Coastal Desert in Southern Africa
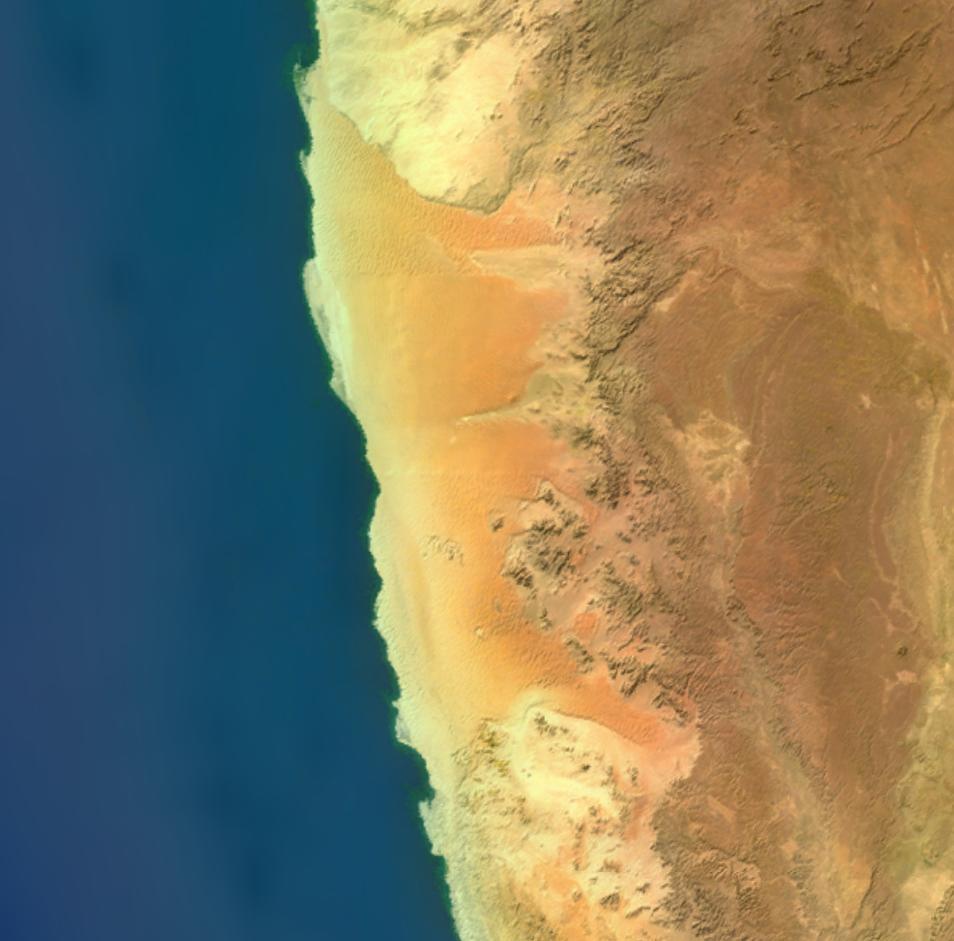
The Namib Sand Sea, located along the Atlantic coast of Namibia, is a remarkable example of a coastal desert and forms part of the wider Namib Desert, which extends into Angola and South Africa. Inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013, the Namib Sand Sea is characterized by extensive fog-influenced dune fields covering an area of more than three million hectares.
The Namib Sand Sea consists of two distinct dune systems. The older, semi-consolidated system lies beneath the younger, active one. These dunes are formed by the transportation of materials thousands of kilometers from the interior, carried by rivers, ocean currents, and winds. The result is a landscape of exceptional beauty, featuring gravel plains, coastal flats, rocky hills, inselbergs within the sand sea, a coastal lagoon, and ephemeral rivers.
One of the most striking aspects of the Namib Sand Sea is its reliance on fog as its primary source of water. This unique environment supports a diverse array of endemic invertebrates, reptiles, and mammals that have adapted to an ever-changing variety of microhabitats and ecological niches. The desert is estimated to be 55–80 million years old, making it the oldest desert globally, surpassing South America's Atacama Desert in age, though the Atacama is often considered the driest.
Annual precipitation in the Namib Sand Sea varies significantly, ranging from just 2 millimeters in the aridest regions to 200 millimeters at the escarpment. Despite these challenging conditions, much of the Namib Sand Sea is protected within Namibia’s Namib-Naukluft National Park, and environmental protection is further reinforced by Namibia’s constitution, which emphasizes sustainable natural resource management.
Geographically, the Namib Sand Sea occupies the central portion of the Namib Desert, extending inland from the Atlantic coast toward the Great Escarpment, where elevation gradually increases. To the north, the Namib Desert continues into Angola’s Moçâmedes Desert, while to the east it transitions into semi-arid landscapes.
Overall, the Namib Sand Sea is a testament to the resilience of life in extreme environments. Its unique combination of geography, climate, and biodiversity make it a vital component of Southern Africa's natural heritage. As a UNESCO World Heritage Site, it serves as a reminder of the importance of preserving these unique ecosystems for future generations.
UNESCO Description of the World Heritage Site
Namib Sand Sea is the only coastal desert in the world that includes extensive dune fields influenced by fog. Covering an area of over three million hectares and a buffer zone of 899,500 hectares, the site is composed of two dune systems, an ancient semi-consolidated one overlain by a younger active one. The desert dunes are formed by the transportation of materials thousands of kilometres from the hinterland, that are carried by river, ocean current and wind. It features gravel plains, coastal flats, rocky hills, inselbergs within the sand sea, a coastal lagoon and ephemeral rivers, resulting in a landscape of exceptional beauty. Fog is the primary source of water in the site, accounting for a unique environment in which endemic invertebrates, reptiles and mammals adapt to an ever-changing variety of microhabitats and ecological niches.
Encyclopedia Record: Namib
The Namib is a coastal desert in Southern Africa. According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namibia, and northwest South Africa, extending southward from the Carunjamba River in Angola, through Namibia and to the Olifants River in Western Cape, South Africa. The Namib's northernmost portion, which extends 450 kilometres (280 mi) from the Angola-Namibia border, is known as Moçâmedes Desert, while its southern portion approaches the neighboring Kalahari Desert. From the Atlantic coast eastward, the Namib gradually ascends in elevation, reaching up to 200 kilometres (120 mi) inland to the foot of the Great Escarpment. Annual precipitation ranges from 2 millimetres (0.079 in) in the aridest regions to 200 millimetres (7.9 in) at the escarpment, making the Namib the only true desert in southern Africa. Having endured arid or semi-arid conditions for roughly 55–80 million years, the Namib may be the oldest desert in the world and contains some of the world's driest regions, with only western South America's Atacama Desert to challenge it for age and aridity benchmarks. Most of Namibia's share of the Namib Desert is protected under the environmental protection included in the constitution of the country.Additional Site Details
Area: 3,077,700 hectares
(viii) — Outstanding example representing major earth stages
(ix) — Outstanding example representing ecological and biological processes
(x) — Contains most important habitats for biodiversity
Coordinates: -24.8852777778 , 15.4077777778